Disk Passthrough to a CT
This guide explains how to assign a dedicated physical disk to a container (CT) in Proxmox VE using ProxMenux. Assigning a full disk to a container is useful when you need isolation, ease of access, or the ability to move the disk between systems, especially for services handling large volumes of data such as Samba, Nextcloud, or video surveillance software, among others.
While it's more common to passthrough entire disks to virtual machines (VMs), there are scenarios where giving full disk access to an LXC container can be very useful.
- A user running a video surveillance system like Frigate or Agent DVR might want recordings saved on a dedicated disk, so they can easily transfer it to another system for review.
- A Nextcloud container might need full disk access to manage user files and take advantage of the entire disk capacity.
- A container may be used for downloads, storing files on a dedicated disk and sharing them over the local network.
- Another use case could be writing backups to an isolated disk.
As you can see, there are many different use cases where assigning a physical disk directly to a CT is the ideal solution.
Description
- Lists physical disks on the Proxmox host, excluding the system disk and mounted system disks.
- Displays all existing LXC containers (CTs) for user selection.
- Allows the user to select one physical disk per execution.
- Formats the disk (with user confirmation) or reuses it, then assigns it as a mount point in the selected CT.
Step-by-Step Instructions
CT Selection
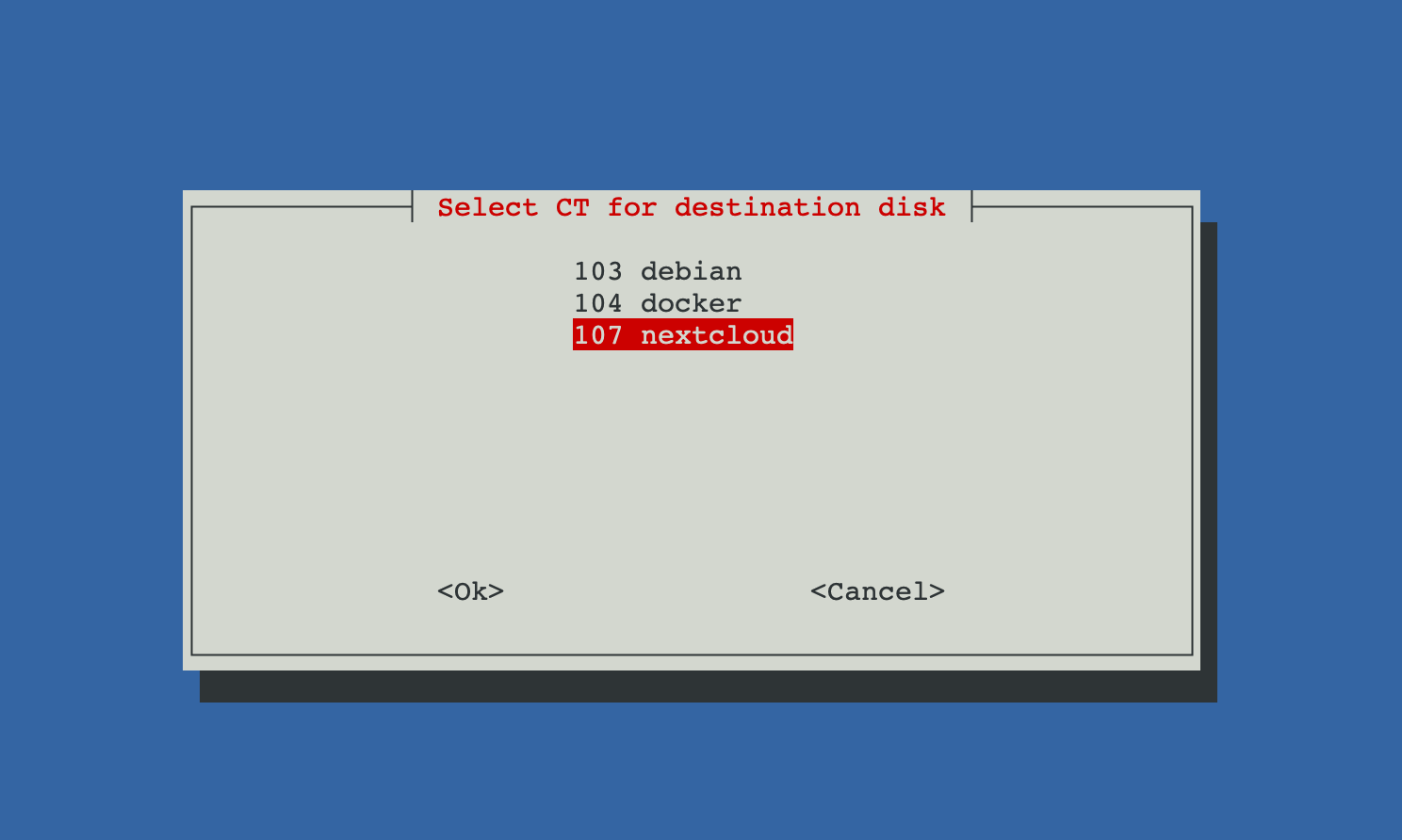
The user selects the destination LXC container (CT) to which the disk will be assigned.
Disk Detection
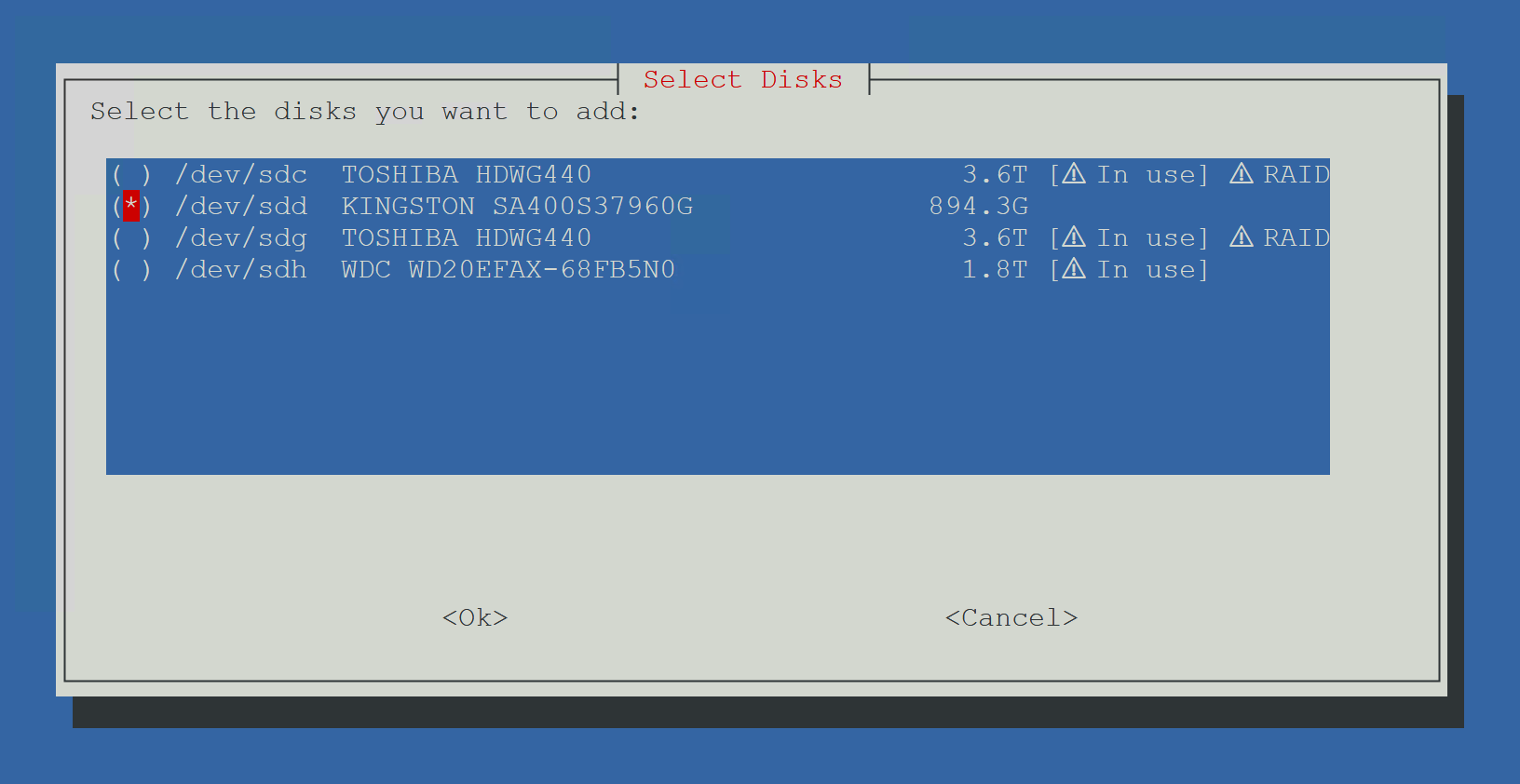
The script lists all physical disks, excluding those used by the system. It also displays metadata like ZFS, LVM, and RAID, and shows warnings if the disk is already in use.
Disk Preparation
The script performs the following actions:
- Detects whether the disk has a supported filesystem (ext4, xfs, btrfs).
- Offers to format the disk if no valid filesystem is found.
- Prompts the user to define the mount point (e.g.
/mnt/disk_passthrough).
Assignment to CT
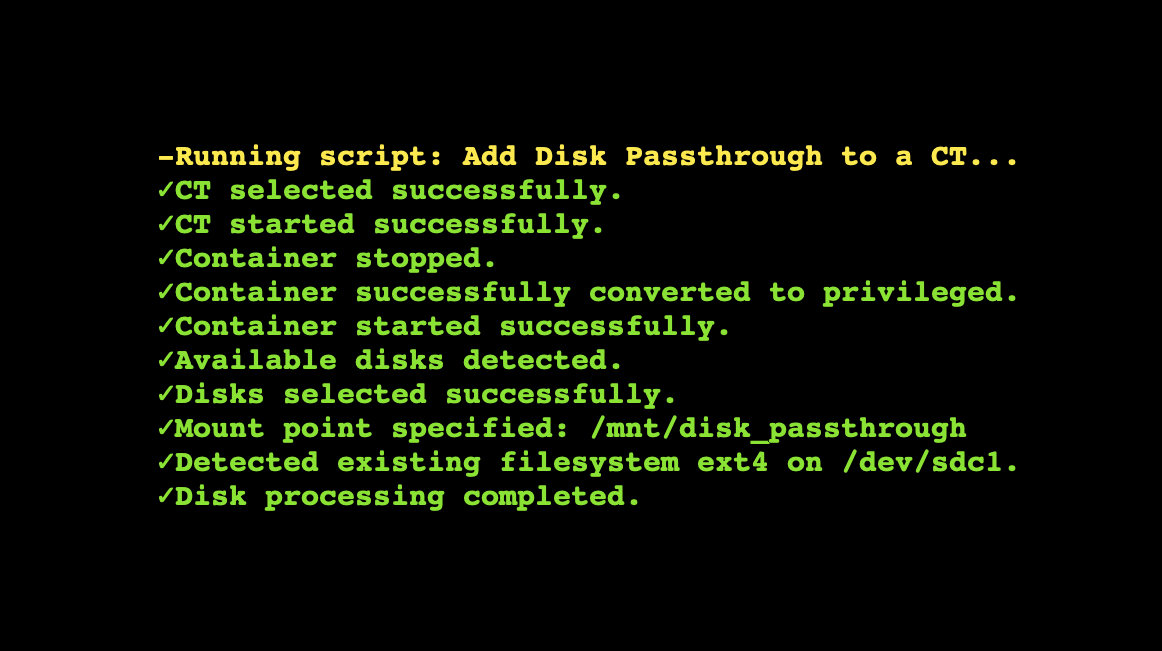
The selected disk is mounted inside the container at the specified path, and permissions are set automatically.
Expected Results
- The selected disk is successfully mounted and accessible within the specified container.
- The script shows a summary of the operation, including any warnings or errors.
- The container can use the assigned storage immediately.
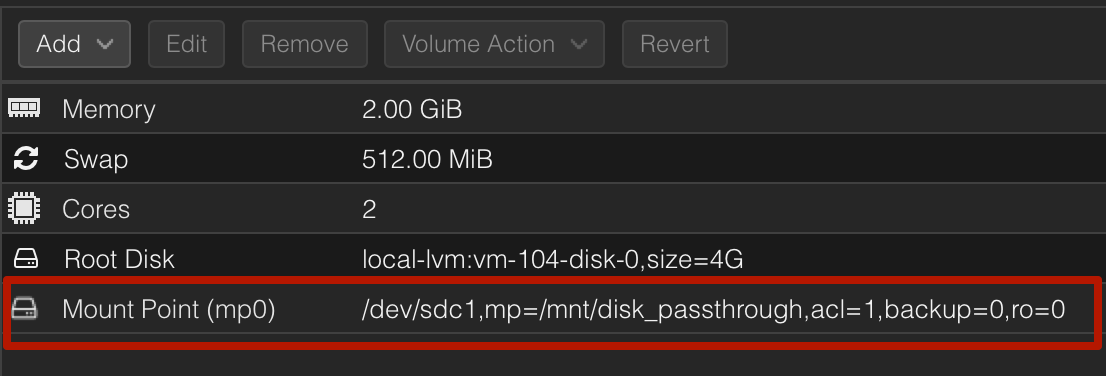
Important Considerations
Important:
The container must be privileged to allow direct read/write access to the physical disk.
- Only one disk can be assigned per script execution.
- Avoid assigning the same disk to multiple VMs or CTs that may run at the same time, as this can lead to data corruption or file loss.
- Clean any RAID, ZFS, or LVM metadata manually before assigning the disk.