Linux VM Creator Script
ProxMenux provides automated scripts that create and configure Linux virtual machines on Proxmox VE. These scripts simplify the process by handling the necessary configurations and optimizations for various Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and many others.
Script Overview
The Linux VM creation script automates the process of setting up virtual machines optimized for running Linux operating systems. The script handles all aspects of VM configuration, including hardware allocation, disk setup, and boot options.
The script simplifies the VM creation process by offering the following options:
- Selection of default or advanced configuration
- Configuration of CPU, RAM, BIOS, and machine type
- Choice between virtual disk or physical disk passthrough
- Selection of disk interface type (SCSI, SATA, VirtIO, or IDE)
- Automatic configuration of EFI for UEFI boot
- Multiple installation methods: official ISOs, Cloud-Init, or local ISO
Default and Advanced Configuration
The script offers two configuration modes:
Default Configuration
If you select default configuration, the script will automatically apply the following values:
| Parameter | Default Value |
|---|---|
| Machine Type | q35 |
| BIOS Type | OVMF (UEFI) |
| CPU Type | Host |
| Core Count | 2 |
| RAM Size | 4096 MB |
| Bridge | vmbr0 |
| MAC Address | Automatically generated |
| Start VM on Completion | No |
If you want to customize the configuration, select the Advanced Settings option in the menu.
Advanced Configuration
If you select advanced configuration, the script will allow you to customize each parameter:
| Parameter | Options |
|---|---|
| Machine Type | q35 or i440fx |
| BIOS Type | OVMF (UEFI) or SeaBIOS (Legacy) |
| CPU Type | Host or KVM64 |
| Core Count | Number of CPU cores |
| RAM Size | Amount of memory allocated to the VM |
| Bridge | Network bridge for connection |
| MAC Address | Custom MAC address |
| VLAN | VLAN tag (if used) |
| MTU | Maximum Transmission Unit size |
Disk Interface Selection
The script allows you to choose the disk interface type for both virtual and physical disks:
| Interface Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| SCSI | Modern interface with good performance and features | Recommended for most Linux distributions (includes discard/trim support) |
| SATA | Standard interface with high compatibility | Good general-purpose choice (includes discard/trim support) |
| VirtIO | Paravirtualized interface with highest performance | Best performance for Linux (includes discard/trim support) |
| IDE | Legacy interface with maximum compatibility | Legacy systems only (no discard/trim support) |
Disk Selection
Once the machine is configured, the script allows you to choose between two types of disks:
Virtual Disk
- The script lists the storage options available in Proxmox
- The user selects the disk and size in GB
- The virtual disk is automatically assigned to the VM using the selected interface type (SCSI, SATA, VirtIO, or IDE)
- Multiple disks can be added and will be assigned sequential device numbers (e.g., scsi0, scsi1, etc.)
Physical Disk Passthrough
- The script detects all available physical disks
- The user selects the physical disk or disks they want to use
- The physical disk is directly assigned to the VM via passthrough using the selected interface type (SCSI, SATA, VirtIO, or IDE)
- Multiple disks can be added and will be assigned sequential device numbers (e.g., scsi0, scsi1, etc.)
Additional Features
EFI Disk Configuration
When UEFI BIOS (OVMF) is selected, the script automatically configures an EFI system disk:
- You'll be prompted to select the storage location for the EFI disk
- A 4MB EFI disk is created and attached to the VM
- The disk is formatted appropriately based on the selected storage backend (e.g., raw format for directory-based storage)
ISO Mounting
The script also handles ISO mounting automatically:
- The installation ISO is mounted to the first available IDE slot (typically
ide2) - For VirtIO disk interfaces, the VirtIO drivers ISO can be mounted if needed
QEMU Guest Agent
The script automatically configures QEMU Guest Agent support:
- Enables the QEMU Guest Agent in the VM configuration
- Sets up the necessary communication channel
- Provides instructions for installing the guest agent inside the VM after installation
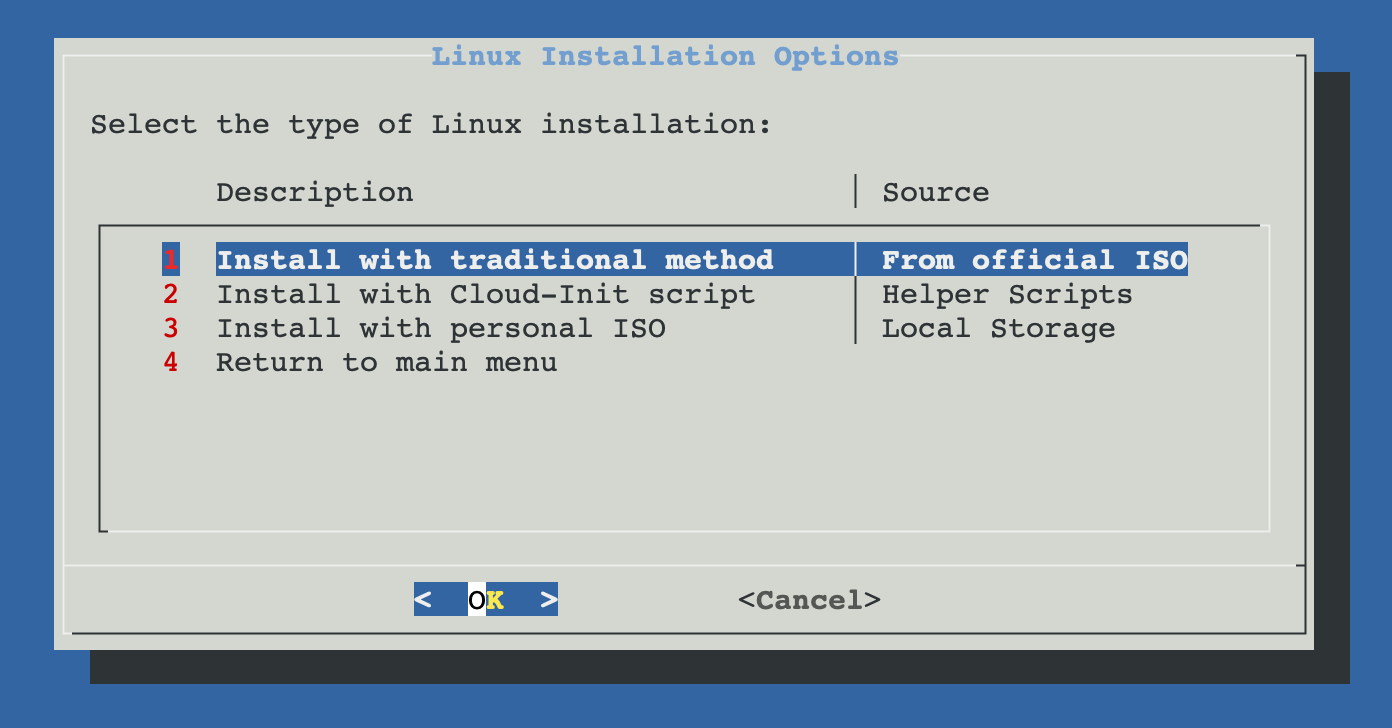
Linux Installation Options
ProxMenux offers three methods for installing Linux on your virtual machine:
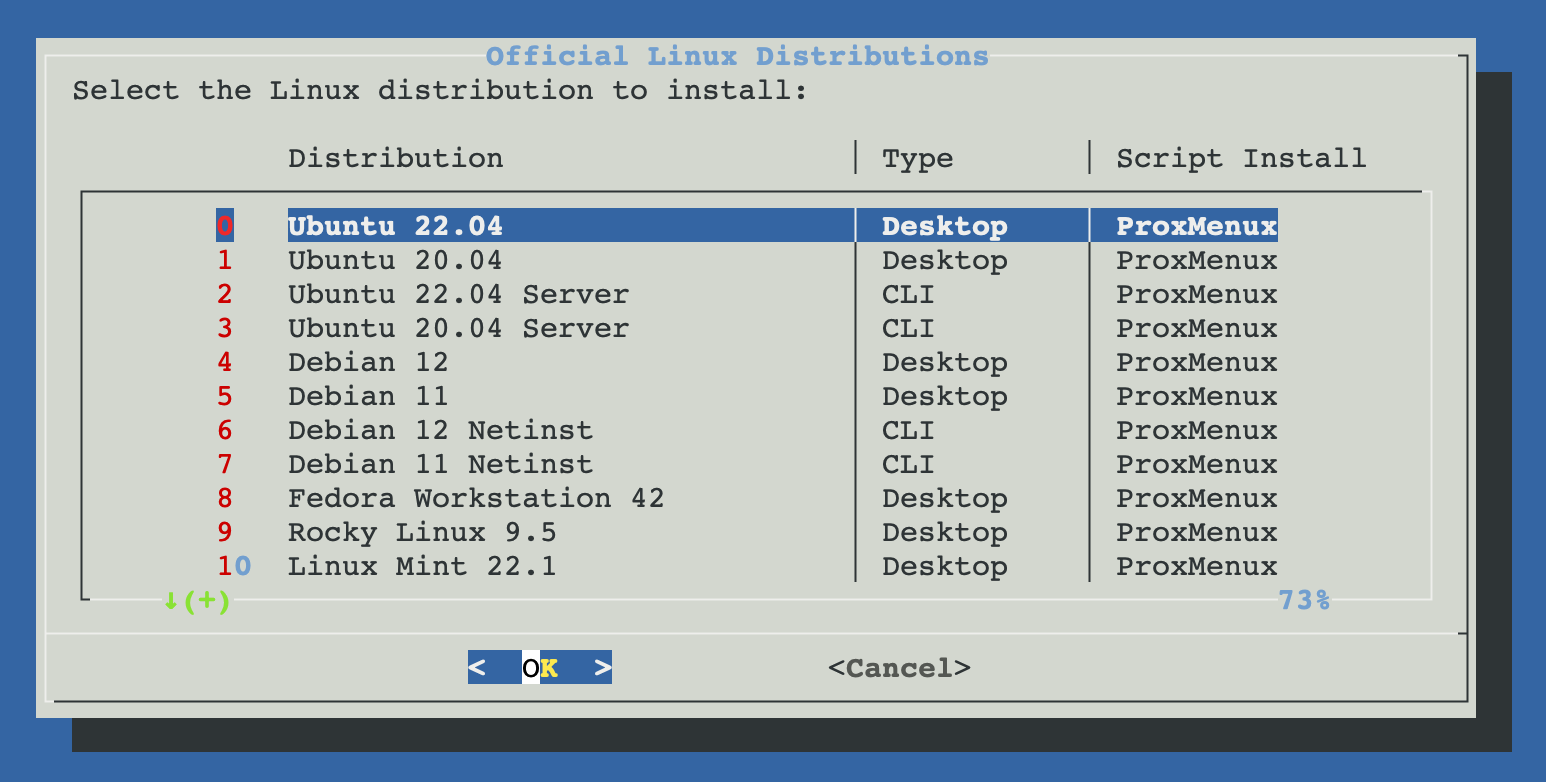
Official ISO Installation
This option allows you to install Linux using official distribution ISOs. ProxMenux provides a curated list of popular Linux distributions that can be automatically downloaded and used for installation.
Available Distributions:
- Ubuntu (Desktop & Server)
- Debian (Full & Netinst)
- Fedora Workstation
- Rocky Linux
- Linux Mint
- openSUSE Leap
- Alpine Linux
- Kali Linux
- Manjaro
Cloud-Init Installation
This option uses Cloud-Init to automate the installation process. It's faster than traditional installation and provides a pre-configured system ready to use.
Available Cloud-Init Images:
- Arch Linux
- Debian 12
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 24.10
External Scripts
Cloud-Init installations use external helper scripts from the community. For more information, visit:
community-scripts.github.io/ProxmoxVELocal ISO Installation
This option allows you to use your own Linux ISO file that's already uploaded to your Proxmox server's local storage. Ideal if you have custom or specific Linux installation media.
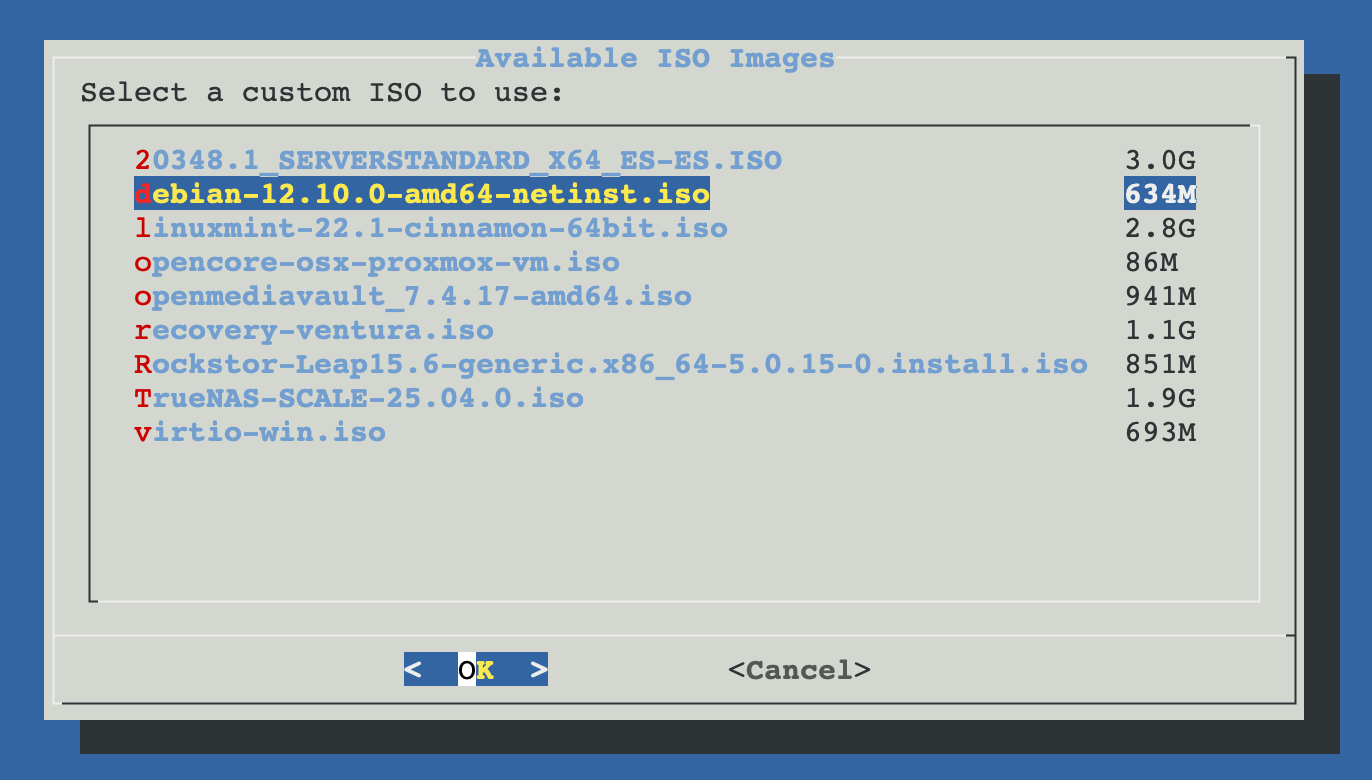
Installation Process
After configuring the VM settings and selecting your installation method, the script will:
- Create the VM with the specified configuration
- Configure EFI disk if UEFI BIOS is selected
- Create and attach virtual disks or pass through physical disks
- Download and mount the Linux ISO (if using official distribution) or mount your local ISO
- Set the boot order (disk first, then ISO)
- Configure the QEMU Guest Agent
- Start the VM if requested
Linux-Specific Tips
Installing QEMU Guest Agent
For better integration with Proxmox, it's recommended to install the QEMU Guest Agent inside your Linux VM. This enables features like proper shutdown, file system freeze for snapshots, and more accurate memory reporting.
Installation commands by distribution:
Debian / Ubuntu:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install qemu-guest-agent -y
sudo systemctl enable qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl start qemu-guest-agentFedora / CentOS / Rocky Linux:
sudo dnf install qemu-guest-agent -y
sudo systemctl enable qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl start qemu-guest-agentArch Linux:
sudo pacman -S qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl enable qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl start qemu-guest-agentopenSUSE:
sudo zypper install qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl enable qemu-guest-agent
sudo systemctl start qemu-guest-agentVirtIO Drivers in Linux
Most modern Linux distributions include VirtIO drivers by default, which means you can use VirtIO disk and network interfaces without additional configuration. This provides the best performance for your Linux VM.
Note:
If you're using an older Linux distribution (pre-2.6.25 kernel) and VirtIO disk interfaces, you might need to load the VirtIO modules during installation. In such cases, you may need to provide a driver disk or use SATA/SCSI interfaces instead.
Optimizing Linux VMs
- Enable disk trim/discard: To enable TRIM support for better SSD performance, add the
discardmount option in/etc/fstabfor your partitions. - CPU type selection: For best performance, use the "host" CPU type which passes through all CPU features from your host to the VM.
- Memory ballooning: Enable memory ballooning to allow dynamic memory allocation. The balloon driver is included in most Linux distributions.
- Use VirtIO network interfaces: VirtIO network interfaces provide better performance than emulated network cards.
Other Linux Systems
ProxMenux provides access to external community scripts that allow the creation of specialized Linux virtual machines for specific use cases:
Home Assistant OS VM (HAOS)
Create a virtual machine that runs Home Assistant OS using a helper script from the community. Ideal for smart home automation.
Docker VM (Debian + SSH + Docker)
Deploy a lightweight Debian-based virtual machine with Docker and SSH pre-installed using an external script.
External Scripts
These installations are handled by community-maintained scripts. For more information or to contribute, visit:
community-scripts.github.io/ProxmoxVE